Advertisement
8. The Point of Yongquan
Advertisement
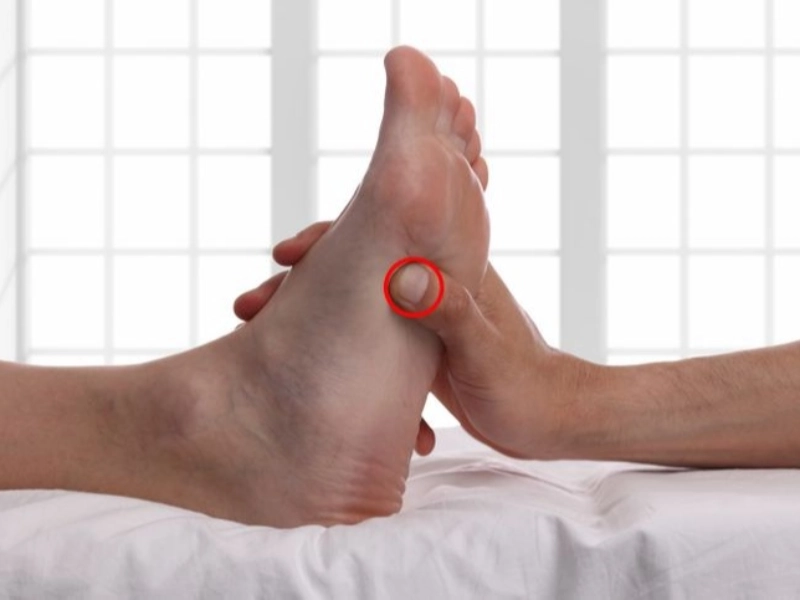
The Yongquan Point, also known as the Kidney 1 or "Bubbling Spring" acupressure point, is located on the sole of the foot, between the second and third toes. This specific point is considered to be a highly influential and versatile pressure point in the practice of traditional Chinese medicine.
To precisely locate the Yongquan Point, start by identifying the webbing between the second and third toes on the sole of the foot. The point can be found in the depression or "valley" that is situated approximately one-third of the way down from the base of the toes. This area is often described as having a slightly indented or "sunken" feel when compared to the surrounding tissue.
When the Yongquan Point is stimulated, either through acupressure, massage, or other techniques, it is believed to have the potential to provide relief for a variety of health concerns. Headaches, motion sickness, and dizziness are some of the most commonly associated conditions that are thought to be alleviated by the activation of this pressure point.
To stimulate the Yongquan Point, one can use their fingertips to apply firm, steady pressure to the area and hold it for approximately one minute. This focused attention on the point is believed to help promote the flow of energy, or "qi," within the body, which in turn can help to restore balance and promote healing.
The use of the Yongquan Point in traditional Chinese medicine is based on the principles of acupuncture and the belief that the body's energy pathways, or meridians, can be influenced through the stimulation of specific points. By targeting the Kidney 1 point, practitioners aim to address imbalances or blockages within the body's energy system, which they believe can contribute to various physical and emotional challenges.
While the scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of acupressure and other energy-based therapies for conditions like headaches, motion sickness, and dizziness is still being explored, many individuals have reported positive experiences with the use of the Yongquan Point. Some studies have suggested that the stimulation of this point may help to improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and alleviate symptoms associated with a variety of health concerns.
It is important to note that the use of the Yongquan Point, or any other acupressure technique, should be done with caution and under the guidance of a trained and experienced practitioner. Improper or excessive stimulation of the point could potentially lead to adverse effects, and individuals with certain medical conditions may need to exercise caution or seek professional advice before attempting to self-treat using this method.
In conclusion, the Yongquan Point, or Kidney 1 acupressure point, is a significant pressure point located on the sole of the foot, between the second and third toes. This point is believed to have the potential to provide relief for headaches, motion sickness, and dizziness when stimulated with firm, steady pressure using the fingertips for approximately one minute. The use of this point in traditional Chinese medicine is based on the principles of energy flow and the belief that the body's energy system can be influenced through the targeted stimulation of specific points.
