The Benefits of Crop Rotation for Home Gardens Overview:
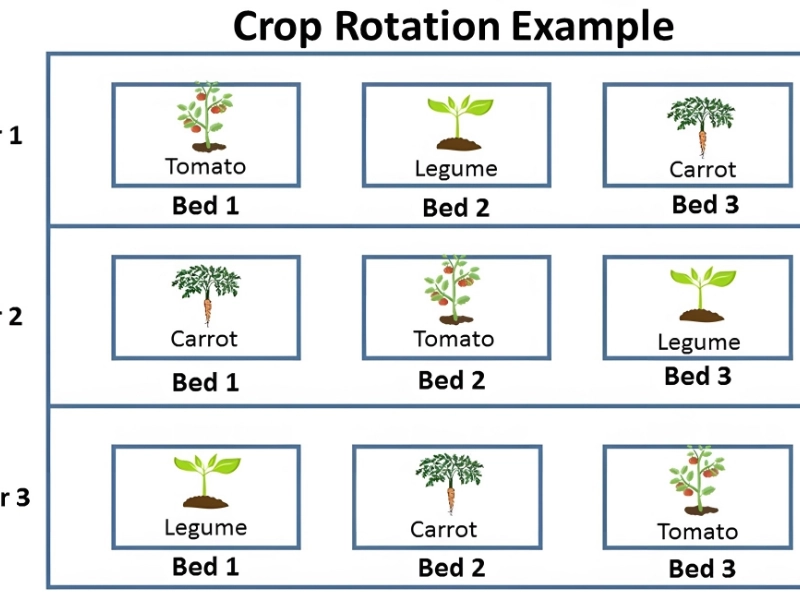
Crop rotation is a gardening practice that involves changing the location of vegetable plants each season. While often associated with large farms, this technique is equally beneficial for home gardens.
Why Rotate Your Vegetables? Soil Fertility:
Different vegetable families have varying nutrient requirements. By rotating crops, you can help maintain balanced soil fertility, as some plants, like legumes, enrich the soil with nitrogen. Pest and Disease Control:
Rotating crops helps disrupt the life cycles of pests and diseases that may thrive in specific plant families. This reduces the likelihood of infestations and infections. Improved Yields:
Healthy soil and reduced pest pressure can lead to better growth and higher yields, making crop rotation a smart strategy for maximizing your garden's productivity. How to Implement Crop Rotation: Rotate by Family: Ensure that vegetables from the same family are not planted in the same spot for at least three to four years. Here are some common vegetable families to consider: Legumes: Beans, peas Nightshades: Tomatoes, peppers, eggplants Chicories: Lettuce, endive Umbels: Carrots, celery Chenopods: Beets, spinach Brassicas: Cabbage, broccoli, kale Allium: Onions, garlic Conclusion: Incorporating crop rotation into your home gardening practices can lead to healthier plants, improved soil quality, and reduced pest problems. By planning your garden layout thoughtfully and rotating your vegetables each year, you can cultivate a more resilient and productive garden. Happy gardening!